

The new pacemaker in the junctional rhythm is the atrioventricular node. In junctional rhythm, the heart beats rate are not controlled by the sinoatrial node.Many conditions as well causes junctional rhythm by creating new pacemaker instead of the sinoatrial node. The junctional rhythm can be originated by many medications that affect the sinoatrial node and make the atrioventricular node an ectopic impulses foci.This sinus rhythm indicates the atria normally contracts before the ventricles.It continues through the bundle of his, Purkinje fibers, and the ventricles ending one heart beat. The electrical impulse starts from the sinoatrial node then travels through the atria. The sinoatrial node in the heart is the pacemaker that determine the rate of the heart beats.The junctional rate may be rapid in which case the rhythm is referred to as a junctional tachycardia.The junctional rate may be slow (40-60 beats per minute) in which case the rhythm is referred to as junctional bradycardia.The juncitonal rate can be accelerated (60-100 beats per minute).The junctional rate is about 40-60 beats per minute.Junctional rhythm can be classified according to the rate of the heart rate as the following:.Pacemaker is indicated for patients with sick sinus syndrome and complete AV block. In children, symptomatic patients can undergo percutaneous radiofrequency ablation. Patients with junctional rhythm due to digoxin toxicity are given atropine and digoxin specific antibody. Patients with sinus node dysfunction should be managed cautiously as the pulse originating from other foci keeps the heart rate. The rhythm here is due to increased vagal tone only. Asymptomatic patients with only juncitonal rhythm and no other cardiac conditions do not require further management. The junctional rate may be rapid in which case the rhythm is referred to as a junctional tachycardia.

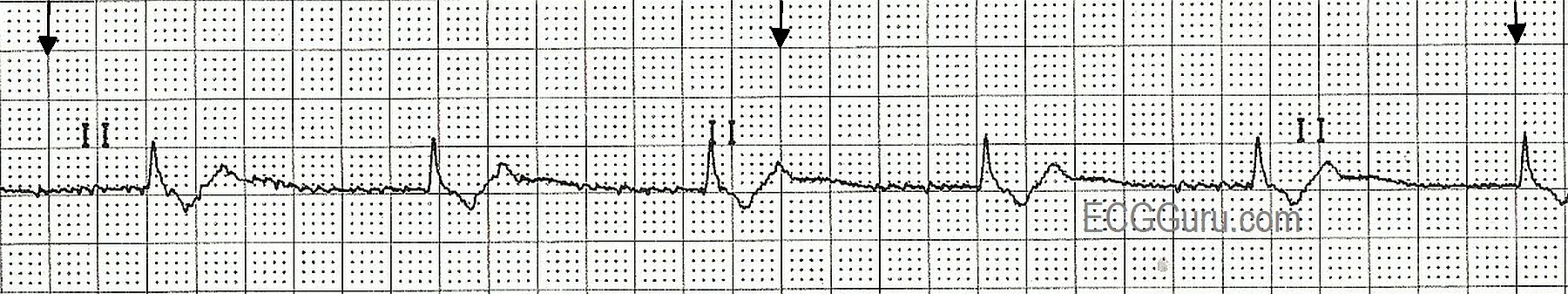
Electrocardiogram may show QRS complexes are narrow as conduction down the His bundle is normal. Physical examination findings of junctional rhythm include pulsating veins and canon a waves in case the right atrium contracting against a closed tricuspid valve. Symptoms of junctional rhythm can be non specific and includes syncope, dizziness, and faitgue. Patients presenting with juncitonal rhythm disease should be asked properly for history of other cardiac conditions as heart failure and sick sinus syndrome. If left untreated, junctional rhythm can lead to syncope and other severe complications. In the United States, the prevalence of junctional rhythm is 166 in 100,000 individuals with sinus node dysfunction. Common causes of junctional rhythm include acute MI, Acute rheumatic fever, antiarrhythmic agents, beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, Complete heart block, Conduction system disease, Digitalis toxicity, Diphtheria, Healthy response during sleep in patients with heightened vagal tone, Heart surgery particularly valve replacement or surgery for congenital heart disease, Ischemic heart disease, Lyme disease, NSTEMI, Sick sinus syndrome, Sinus arrest, Chest trauma, Radiation therapy, Collagen vascular disease, Myocarditis, Clonidine, Reserpine, Adenosine, and Cimetidine. In junctional rhythm, the heart beats rate are not controlled by the sinoatrial node. The junctional rhythm can be originated by many medications that affect the sinoatrial node and make the atrioventricular node an ectopic impulses foci. Junctional rhythm can be classified into junction escape rhythm, accelerated junctional rhythm, junctional bradycardia, and junctional tachycardia. Junctional rhythm describes an abnormal heart rhythm resulting from impulses coming from a locus of tissue in the area of the atrioventricular node, the "junction" between atria and ventricles. See also: Junctional bradycardia for slow junctional rhythms, and junctional tachycardia for fast jucntional rhythms Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Ahmed Elsaiey, MBBCH
List of terms related to Junctional rhythmĮditor-In-Chief: C. Risk calculators and risk factors for Junctional rhythmĬauses & Risk Factors for Junctional rhythm US National Guidelines Clearinghouse on Junctional rhythmĭirections to Hospitals Treating Junctional rhythm Ongoing Trials on Junctional rhythm at Clinical Ĭlinical Trials on Junctional rhythm at Google Most recent articles on Junctional rhythmĪrticles on Junctional rhythm in N Eng J Med, Lancet, BMJĬochrane Collaboration on Junctional rhythm


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
